Pittet Lab
Read BioMy laboratory performs a research program on the host immune response in vivo with the main goal to offer valuable new ways to combat cancer. We use various modalities, including in vivo imaging, to study where, when and how immune cells are produced, traffic, and mediate regulatory or effector functions. The studies make use of both genetic mouse models, which allow manipulations and analyses of mechanisms and causality, and human patient material, to ensure that the results are anchored in clinical correlates. This dual approach gives opportunities for discovery of novel contributions of the immune response to tumor progression, new biomarkers useful for diagnosis and prognosis, and novel targets for therapeutic intervention. Dr. Pittet directs Cancer Immunology Program at CSB and collaborates with several immunology programs at Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital and Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
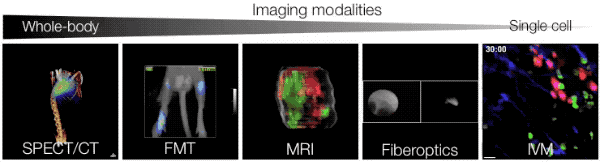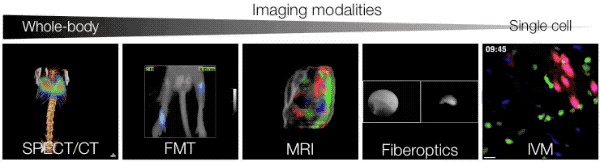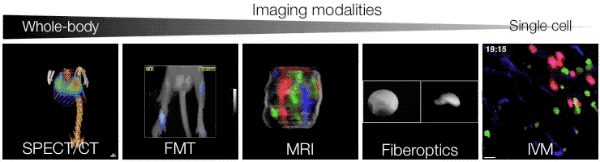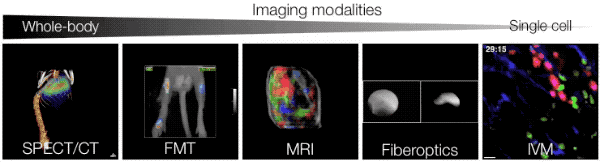
Recent Publications
Zitti B, Duval F, Wirapati P, Hicham M, Xie Y, Oh J, Hoelzl J, Meiser P, Varrone M, Peterson HM, Cianciaruso C, Bill R, Bayerl F, Bolli E, Goubet AG, Kiss M, McDowell S, Cheng P, Celestini D, Terzic J, Zwahlen T, Alouche N, Zouggari N, Tarussio D, Tissot S, Nunes-Hasler P, Mino-Kenudson M, Lanuti M, Faquin WC, Sadow PM, Tille JC, Intidhar Labidi-Galy S, Garris CS, Hugues S, Petrova TV, Ludewig B, Quezada S, Luther S, Mempel TR, Ciriello G, Pai SI, Michielin O, Böttcher JP, Weissleder R, Pittet MJ
Positioning and reversible suppression of CCR7+ dendritic cells in perivascular tumor niches shape cancer immunity. Immunity. 2025;59(1):161-176.e12 - PMID: 41421339 - PMCID: PMC12882814 - DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2025.11.020Deutsch-Williams RJ, Xie Y, Rabinowitz Z, Goemans M, Wirapati P, Vinegoni C, Carlson JCT, Pittet M, Weissleder R
Targeting cancer- associated fibroblasts for real- time intraoperative tumor identification with a spray-on fluorescent probe. Sci Adv. 2025;11(47):eaeb5810 - PMID: 41259533 - PMCID: PMC12629203 - DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aeb5810Oh J*, Hoelzl J*, Carlson JCT, Bill R, Peterson HM, Faquin WC, Pittet MJ, Pai SI, Weissleder R
Spatial analysis identifies DC niches as predictors of pembrolizumab therapy in head and neck squamous cell cancer. Cell Rep Med. 2025;6(5):102100 - PMID: 40311615 - PMCID: PMC12147904 - DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102100Qin T, Mattox AK, Campbell JS, Park JC, Shin KY, Li S, Sadow PM, Faquin WC, Micevic G, Daniels AJ, Haddad R, Garris CS, Pittet MJ, Mempel TR, ONeill A, Sartor MA, Pai SI
Epigenetic therapy sensitizes anti-PD-1 refractory head and neck cancers to immunotherapy rechallenge. J Clin Invest. 2025;135(6):ePub - PMID: 40091844 - PMCID: PMC11910227 - DOI: 10.1172/JCI181671Qiu W, Dincer AB, Janizek JD, Celik S, Pittet MJ, Naxerova K, Lee SI
Deep profiling of gene expression across 18 human cancers. Nat Biomed Eng. 2024;9(3):333-355 - PMID: 39690287 - DOI: 10.1038/s41551-024-01290-8- More publications ...
Research projects
Tumor microenvironment
 In vitro studies often do not reliably predict the behavior of cells in vivo. Therefore our goals are: (a) to study cellular players directly in situ by means of appropriate bioimaging technologies, (b) to quantify and model information obtained by bioimaging, (c) to develop approaches for comprehensive investigation of various cell types in defined microenvironments. In cancer, a number of immune and nonimmune cell types respond to tumor stimuli and exhibit complex regulatory or effector functions, for example through cell-cell contact and/or secretion of soluble factors. We use recent advances in in vivo imaging to yield new insights into the biology of host cells with the ultimate goal to quantify cellular responses in vivo. As detailed below, we have focused our efforts on the study of T cell responses (anti-tumor CTL and suppressor Treg cells) and monocyte responses (monocyte subsets with distinct inflammatory potential and their lineage descendants).
In vitro studies often do not reliably predict the behavior of cells in vivo. Therefore our goals are: (a) to study cellular players directly in situ by means of appropriate bioimaging technologies, (b) to quantify and model information obtained by bioimaging, (c) to develop approaches for comprehensive investigation of various cell types in defined microenvironments. In cancer, a number of immune and nonimmune cell types respond to tumor stimuli and exhibit complex regulatory or effector functions, for example through cell-cell contact and/or secretion of soluble factors. We use recent advances in in vivo imaging to yield new insights into the biology of host cells with the ultimate goal to quantify cellular responses in vivo. As detailed below, we have focused our efforts on the study of T cell responses (anti-tumor CTL and suppressor Treg cells) and monocyte responses (monocyte subsets with distinct inflammatory potential and their lineage descendants).
Adaptive immune cells
Innate immune cells
Mononuclear phagocytes exert crucial functions as scavengers and can trigger or regulate immune responses. Recent studies indicate that monocytes - the precursors of macrophages and dendritic cells - comprise separate subsets that 'commit' to specific functions. The activity of these subsets in vivo is largely unknown. We are studying tissue tropism, cellular differentiation and role in immunity of monocyte subsets in various inflammatory conditions. We are also testing whether these cells are potential targets in therapy.
News
Mikael Pittet, PhD, has been promoted to Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School. Congratulations Mikael!
Congratulations to Jeremy Gungabeesoon (Pittet lab) for becoming a 2019 Landry Cancer Biology Fellow at Harvard University. This is a big honor!
"Discovering Myeloid Cells in Lung Tumors" - Our work from the Pittet lab and Klein lab is out! See also interview with the authors.
Five CSB PIs are on the list of Highly Cited Researchers of 2018. Congratulations to Brad Bernstein, Matthias Nahrendorf, Mikael Pittet, Fil Swirski, and Ralph Weissleder!
“A small population of immune cells is key for successful cancer immunotherapy” - Study by Garris et al. from the Pittet Lab. See also interview with the authors.