Nahrendorf Lab
Read BioThe Nahrendorf laboratory focuses on the role of immunity in cardiovascular health and disease, specifically in atherosclerosis and heart failure. Of particular interest are the function, supply and production of leukocytes, and the signals that regulate hematopoiesis after injuries such as myocardial infarction or stroke. We described that after MI, the spleen releases a large population of ready-made leukocytes that travel to the ischemic heart (Science 2009, New York Times 2009). We further found that MI, chronic stress and sedentary life style modulate the hematopoietic stem cell niche, activating migration and proliferation of myeloid progenitor cells (Nature 2012, Nature Med 2014, Nature Med 2019). Resident macrophages, on the other hand, do not derive from circulating cells and promote steady state functions such as cardiac conduction (Cell 2017). The laboratory also develops and employs imaging to sample biology non-invasively, using MR, nuclear, optical and microscopic modalities.

Recent Publications
O'Shea A, Lewis AJM, Caravan P, Izquierdo-Garcia D, Le Fur M, Catalano OA, Montesi SB, Quintana JM, Carlson JCT, Dubach JM, Castro CM, Bobić M, Huesa-Berral C, Ng TSC, Bertolet A, Nahrendorf M, Weissleder R
First-in-Human Study of the Carbohydrate Nanoparticle 64Cu-Macrin. J Nucl Med. 2025;:ePub - PMID: 41469153 - DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.125.270770Nahrendorf M, Robbins C
Macrophage Mayhem in Aortic Aneurysm. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2025;10(12):101432 - PMID: 41432338 - PMCID: PMC12861633 - DOI: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2025.101432Nahrendorf M, Kumowski N, Steffens S
Neutrophils in Myocardial Infarction. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2025;10(11):101408 - PMID: 41298044 - PMCID: PMC12790144 - DOI: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2025.101408Nahrendorf M
Recognizing Early Career Translational Investigators. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2025;10(11):101410 - PMID: 41298046 - PMCID: PMC12790141 - DOI: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2025.101410Jang HJ, Kim J, Kim H, Kim T, Chung J, Cremer S, Krohn-Grimberghe M, Kim EJ, Schellingerhout D, Nahrendorf M, Kim DE
Inhibiting Monocyte Migration Reduces Arterial Thrombosis and Facilitates Thrombolysis. Stroke. 2025;56(12):3438-3453 - PMID: 41070446 - PMCID: PMC12636086 - DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.125.052352- More publications ...
Research projects
Leukocytes in cardiovascular health
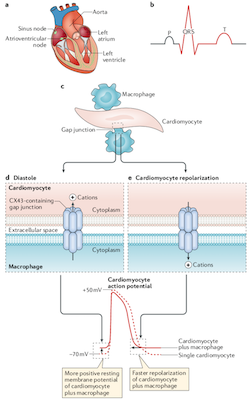
The Nahrendorf laboratory shares a longstanding interest with the Swirski lab in innate immune cells, especially myeloid cells. We discovered that healing after myocardial infarction involves time-resolved monocyte and macrophage subset dynamics. We identified a splenic monocyte reservoir, which deploys within 24 hours after myocardial infarction. This reservoir contributes half of all monocytes recruited to the infarct. In atherosclerosis and chronic heart failure, macrophages expand by proliferating locally, and there is interaction between local and systemic inflammation, including in the remote myocardium after ischemic injury. In the healthy heart, cardiac resident macrophages connect to myocytes via gap junctions and participate in electric conduction; their depletion leads to conduction abnormalities such as AV block.
Activation of hematopoiesis in cardiovascular disease
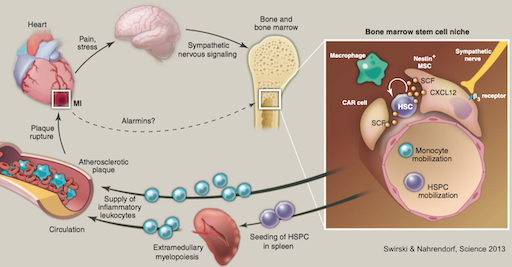
We described the mechanisms behind acceleration of atherosclerotic disease after a first infarct in the heart or brain. Infarct-induced sympathetic nervous system signaling in the bone marrow activates hematopoietic stem cells, which begin to proliferate and relocate to the spleen where they over-produce leukocytes. The most upstream point of hematopoiesis activation rests in CCR2+ hematopoietic stem cells. Newly produced leukocytes migrate to the atherosclerotic plaque, rendering it more inflamed and vulnerable to rupture, triggering reinfarction, a frequent clinical event that was previously unexplained. The findings are clinically important as they provide a new therapeutic opportunity to prevent secondary complications of atherosclerosis. We subsequently observed similar pathway activation after ischemic stroke and during exposure to chronic psychosocial stress.
In vivo RNAi for immunomodulation
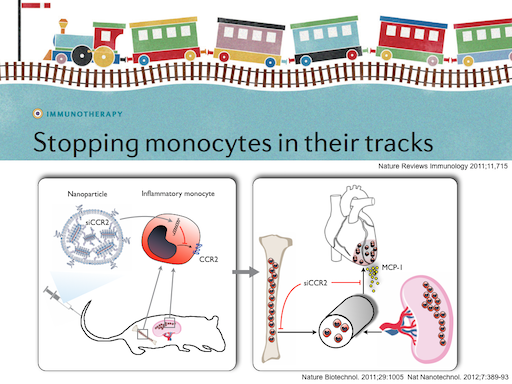
In collaboration with MIT and Alnylam, we pioneered in vivo RNAi to silence the chemokine receptor CCR2, and subsequently other targets, in monocytes, macrophages and endothelial cells. Delivered by nanoparticles, siRNA is incorporated into splenic and circulating monocytes and macrophages, resulting in efficient silencing of gene expression. These cells 'lose their GPS', i.e. they are no longer able to migrate to the site of inflammation. This new class of anti-inflammatory therapy is highly selective, as it only targets certain genes. Subsequently we have targeted other proteins in myeloid cells and their progenitors as well as endothelial cells.
News
Please join us in congratulating Ralph Weissleder, MD, PhD and Matthias Nahrendorf, MD, PhD for being recognized as Highly Cited Researchers in 2025.
Clarivate Analytics’ Highly Cited Researchers List is an annual report of individuals at universities, research institutes and commercial organizations who demonstrate a significant and broad influence in their field or fields of research.
The American College of Cardiology announced today the appointment of Matthias Nahrendorf, MD, PhD, as the new Editor-in-Chief of JACC: Basic to Translational Science.
Please mark your calendars: A highlight for the imaging interested cardiovascular community will happen on October 23rd 2025 at Assembly Row. The Gordon Center and i3 are jointly hosting the symposium “Frontiers in Cardiovascular Imaging: Innovations, Insights, and Impact”. We are excited that Jim Brink, Peter Libby, Rob Gropler, Kory Lavine, David Sosnovik, Farouc Jaffer and Ahmed Tawakol are confirmed to present! Stay tuned for the final agenda, venue and registration.
Nahrendorf Lab has been selected to receive one of the Leducq Foundation International Networks of Excellence Awards for 2024.
Kamila Naxerova, PhD received the 2022 Howard Goodman Fellowship Awards. The project is titled “Defining the Evolutionary Characteristics of Human Metastasis Across Space and Time.” The Goodman Award is an endowed fellowship established by the MGH Department of Molecular Biology in honor of its founding chief, Howard M. Goodman, PhD