Research Focus
Imagine, if we understood what the 30 trillions of cells in our body do at any given moment...
Now compare these 30 trillions of cells (not counting the microbiome!) to the earth population of 8B people (3,750 times more!). This creates a massive undertaking...
At CSB we develop innovative technologies to enable the discovery of new biology, drug targets and diagnostics.

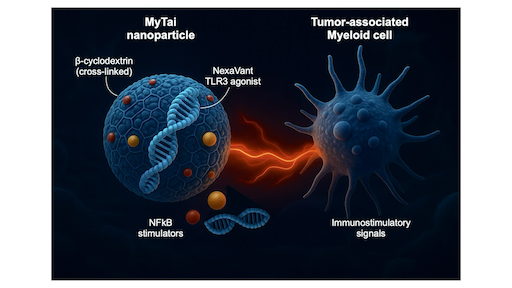
Reprogramming Tumor-associated Myeloid Immunity through MyTai
Most cancers create immunosuppressive environments dominated by tumor-associated myeloid cells that silence T-cell activity. To overcome this, our team developed called MyTai (a myeloid-targeted immune enhancer cocktail) that reprograms these cells into powerful immune activators. In a study published in ACS Nano (2025), the team introduced a carbohydrate-based nanoparticle system that combines a refined viral RNA agonist (NexaVant, NVT) with two small-molecule immune stimulators: R848 (a TLR7/8 agonist) and LCL161 (a non-canonical NF-κB activator). Unlike lipid nanoparticles, MyTai’s cyclodextrin-based carrier avoids cationic lipids, dramatically reducing systemic toxicity while maintaining efficient delivery to tumor-associated macrophages and dendritic cells. Learn more...
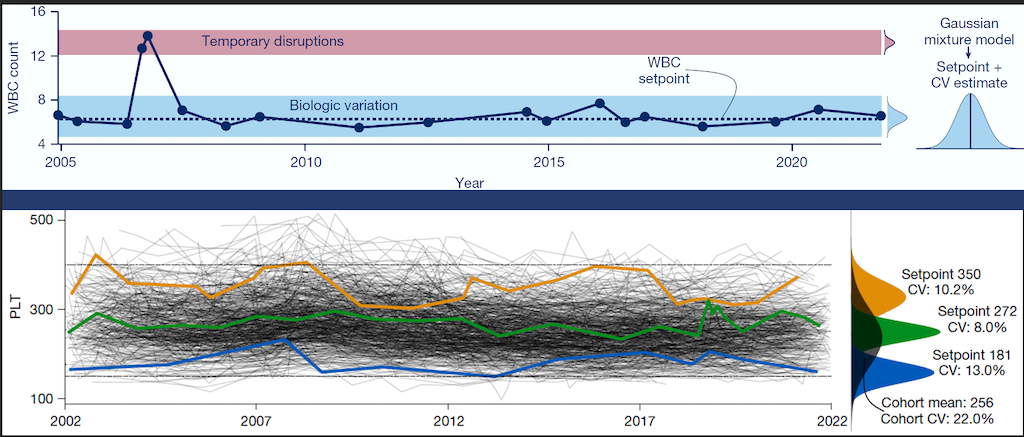
Personalized Blood Count Ranges for Precision Medicine
The complete blood count (CBC) is an important screening tool for healthy adults, but results are usually interpreted relative to one-size-fits-all reference intervals, undermining the precision medicine goal to tailor care for patients on the basis of their unique characteristics. CSB researchers studied thousands of patients at MGH and found that routine CBC indices fluctuate around stable values or setpoints, and setpoints are patient-specific, with the typical healthy adult’s setpoints distinguishable from those of 98% of other healthy adults, and these differences persist for at least 20 years. Setpoints in apparently healthy adults were associated with significant variation in clinical risk. Setpoints also define patient-specific reference intervals and personalize the interpretation of subsequent test results. This study shows CBC setpoints are sufficiently stable and patient-specific to help realize the promise of precision medicine for healthy adults. Learn more...

Closer look into EV mRNA through SCOPE
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) in blood samples can provide valuable information about cancer heterogeneity and progression without invasive procedures. EV mRNA is particularly useful, offering insights into mutations, drug resistance, and recurrence. However, detecting EV mRNA has been challenging due to its scarcity in clinical samples. CSB researchers have developed SCOPE (Self-amplified and CRISPR-aided Operation to Profile EVs) to address this issue. By innovatively using CRISPR technology, SCOPE can detect single-base mutations in just a drop of blood. In early clinical studies, SCOPE successfully monitored tumor recurrence in colorectal cancer patients and classified glioblastoma patients. This technology could accelerate clinical decision-making and improve the use of EVs in personalized cancer treatment. Learn more...